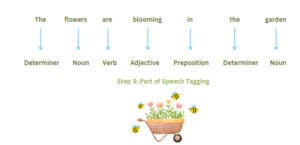
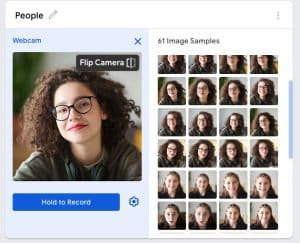
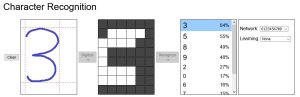
Introduction to AI Machine Learning via Teachable Machines
 Grade 4 - Grade 6
Grade 4 - Grade 6
Students explore aspects of AI and develop their own simple AI programs. Then, they connect their newfound knowledge to real-world examples.