Section Navigation
Introduction
This module will teach students how to model something more complex, duplicate, and hide objects. As well as introduce more tools that Blender uses to edit objects.
Learning Goals
The learning goal of this module is to add more books to a bookcase to get closer to a final product.
Curriculum Links
This module provides an opportunity to address curriculum expectations in the Arts, Computer Studies and Math Grades 9 to 12 expectations. In particular, students will have an opportunity to develop spatial thinking skills, investigate geometric relationships and use a new software programme (Blender). This assignment will also demonstrate how art and engineering come together to create 3D characters and objects when telling a story.
Guiding Questions
- What is 3D modeling?
- Where do you see 3D modeling being used today?
- What is the difference between 3D and 2D?
Vocabulary
ViewPort - This is where you see all of the objects of your scene.
Axis - Axis’ are imaginary lines that help us and the computer navigate 3D space.
Orbiting - Rotating your view around a fixed point or object.
Panning - Sliding the view up down left and right.
Pivot Point - The red blue and green arrows that appear on an object when it is selected. Usually the center of an object and is where the object is moved, rotated or scaled from.
Translate - Sliding an object in 3D space.
Rotating - Turning an object in 3D space.
Scale - Manipulating the size of an object in 3D space.
Mesh - A mesh is a collection of vertices, edges, and faces that describe the shape of a 3D object.
Vertex - A vertex is a single point (the plural of vertex is “vertices”).
Edge - An edge is a straight line segment connecting two vertices.
Face - A face is a flat surface enclosed by edges (some other applications call these “polygons”).
UV Mapping - UV mapping is the 3D modeling process of projecting a 2D image to a 3D model’s surface for texture mapping. The letters “U” and “V” denote the axes of the 2D texture because “X”, “Y” and “Z” are already used to denote the axes of the 3D object in model space.
Materials
- Blender – Download Blender
- Paper
- Scissors
- Tape
- Coloured pencils
Computer Activity
Part 1 – Blenders Interface Refresher
To begin set Blender to Factory Settings. Under File (top left of your screen) select Load Factory Settings. This should display a camera, light, cube, and a grid.

You will notice there is a blue, green, and red line. These are your axis , you can remember these by:
- Blue = Z
- Red = Y
- Green = X
To demonstrate how we can use the interface to our advantage, we are going to close and move some windows.
- Left side of the screen: Our toolbar. This is used to edit and create objects. For this we won’t be needing it open. You can close it by hitting T on your keyboard.
- Right side of the screen: This is our properties and Layers tab. We also won’t be using these for this project. To do this drag the triangle in the corner of your 3D viewport into the properties tab.
- Bottom of the screen: another toolbar. To demonstrate how this works we can move the toolbar to the top of the page by right clicking inside of the toolbar and selecting “flip to top”
Moving in your scene is easier than you think. It’s all in your mouse.
- Left click: 3D cursor in Object Mode, you can also move parts of your object with left click in Edit Mode.
- Middle Mouse Button: Orbits around the object.
- Zoom: You can zoom in and out with the middle mouse wheel and scrolling.
- Panning: Holding Middle Mouse Button and Shift you can move vertically and horizontally across the screen.
- Right click: Select parts of your object in Edit Mode, free move in Object Mode.
Part 2 – Modeling, UV Mapping, Painting
In the first part of the “Introduction to Blender Part 1” we learned how to make a case. Now we are going to model a couple books to put on our case.
For this module we will be using Object Mode, Edit Mode, and Texture Paint Mode.
- In our scene we should already have our bookcase. Here I just painted mine brown in Texture Paint Mode.
- Now we are going to go back into Object Mode. Here we are going to add another cube by using “Shift+A” then go to Mesh>Cube. Make sure we are back to viewing our solid shape instead of viewing our texture.
- In Object Mode we are going to scale down our object to fit inside of a bookcase. We can use “S” to scale, then use our 3D widget to move our cube into the bookcase to see how small it is.
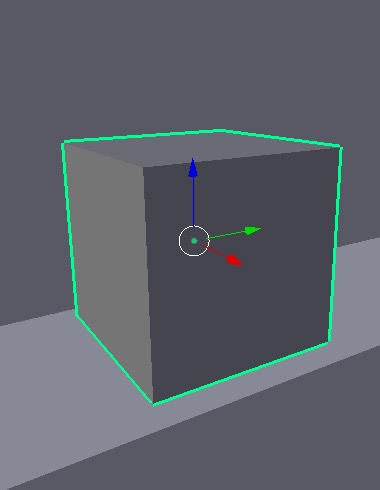
- Now we can scale on the X,Y,Z axis. If we hit “S” on our keyboard and then hit “X” “Y” or “Z” it will scale on those axises, if you make a mistake or want to cancel a movement use “esc” on your keyboard.
- This is what my book looks like on the shelf:
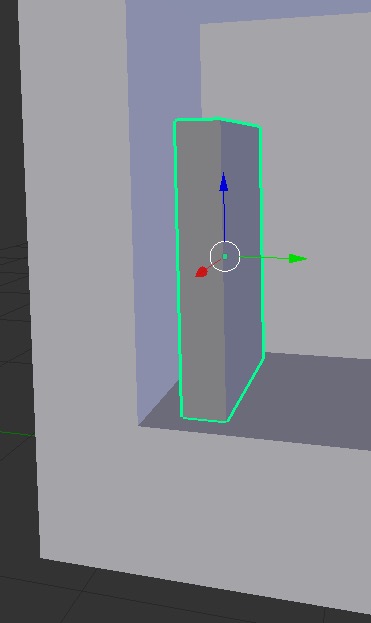
- Now we are going to hide our case so we can view our book better. If you right click to select your case then hit “H” on your keyboard this will hide our object.
- Now select the book and hop into Edit Mode using tab. Here we are going to be adding a divot inside of the book to make it look like our book has more dimension.
- Using the knife tool in our toolbar “T” we are going to be making custom loop cuts. To do this we will make smaller rectangles inside of the book.
- Left click to make cuts in your object and hit the spacebar to confirm the cuts. Here is what mine looks like, the top and bottom have the same cuts.
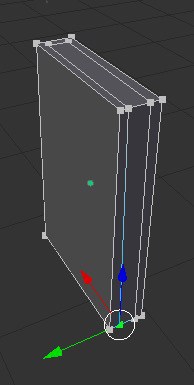
- Now we are going to delete the side face, using face select

- we are going to select the face and delete it using X>Faces.
- Now we are going to extrude the top and bottom face inwards. To do this use “E” and drag your mouse until the face is inverted, then left click to confirm.
- We have a missing face now. To fix this we will be using the edge select tool

- and selecting the two edges from the top and bottom and hitting “F” on our keyboard to fill it in. Here is what it should look like:
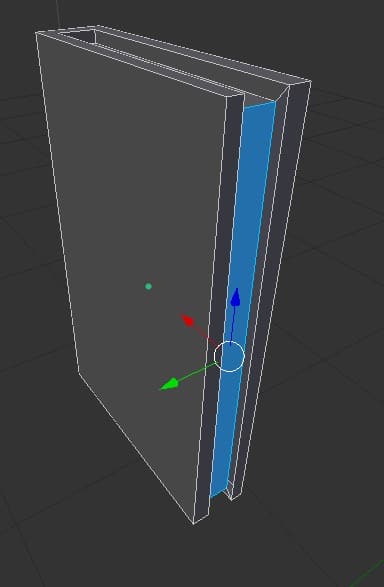
- Now we can unwrap our object! Just like we did for the bookcase we are going to make sure we still have our “UV/Image Editor” window open. Then we will be using “AA” to select all of our object. Then use “U” to Smart UV Unwrap the book.
- Then it’s time to paint our book in Texture Paint Mode. Make sure you are viewing your texture.
- It will be white until we “Add Paint Slot” and choose a Diffuse Map. Now go crazy and paint the book however you want.
- Once we are done we are going to unhide the bookcase to our scene. To do this just use the Properties menu, here we can see the different objects we have. Click on the Eye to view the bookcase again.
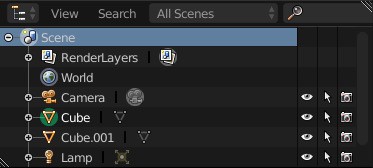
- Our case might not display our texture on it, to fix this make sure you select the case by right clicking on it, then go into Texture Paint Mode to show the texture.
- If you want to duplicate your books to make the shelf look full you can use “Shift+D” then move it on the X axis by hitting “X” on the keyboard. This has to be done in Object Mode so that we can select the object.

Conclusion
This lesson was intended to introduce students to 3D modeling in Blender. While this is only an introduction of what you can do with blender, it is great for students have a better understanding of how you can use Blenders interface.
Resources
Additional Resources
- Blender Tutorials are great for beginners.
Social Media Resources
- Blender on Twitter – @blender_org